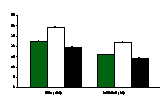
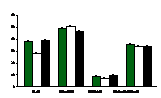

THE MICHIGAN ASH MONITORING
PROJECT: EVALUATING MICHIGANS ASH RESOURCE
SARAH E. BRODEUR-CAMPBELL1,
JESSICA A. METZGER1, JOHN A. WITTER2,
ANDREW J. STORER1
1 SCHOOL OF FOREST RESOURCES AND ENVIRONMENTAL
SCIENCE, MICHIGAN TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY, HOUGHTON MI 49931
2 UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN, ANN ARBOR MI



Objective: Evaluate the health and
sustainability of the ash resource in Michigan before, during, and after the spread
of emerald ash borer through the range of ash (Fraxinus spp).
Characterize changes in the
forest matrix caused by the spread of an invasive forest pest with the
capability to remove its host tree from the landscape.
Characterize interactions among
emerald ash borer and native pests and diseases.
Methods: Eighty (80) plots marked using
GPS and laid out using standardized transects with 15 ash trees measured per
transect.

ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Funding for this project comes from the USDA Forest Service, Northeastern Area, State and Private
Forestry. Our thanks to Seri Robinson, Terrence Smith, Matt Abbotts, Helana
Nelson, Rob Benson, and Eric VanWormer for help with data collection.
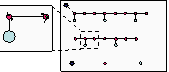
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
9 10
11 12 13
14 15
Typical plot layout. Numbers indicate prism point number.
= witness point, = prism point, and = vegetation circle & soil
collection point
22 m
4 m
2.27 m
radius
Non-ash tree
Ash tree


Results
of ANOVA run on tree data values:
Significant site*species interactions:
Vigor - site quality for that species.
DBH and height - general tree size differs depending on species response at each
site.
Foliage transparency - leaf production differs depending on species response at each
site.
Significant differences among species
independently of site:
Crown density - depends on
species.
Significant differences among sites
independently of species:
ULCR, density, and light exposure may be
functions of site openness.
Affected by site management and
stand density.
Crown dieback - intra-site factors like age or disease may be affecting all ash at a
particular site.
No significant differences between sites or
between species:
Crown class - similar functional role and
position of different ash species in the canopy at each site.
Overall
Ash Condition
Overall
health in UP is good.
Vigor averages: 1.32 to 1.48, with standard error between 0.04-0.05.
All three species of ash perform
well when on suitable sites.
The apparent
health of ash may present challenges to the establishment of emerald ash
borer in the Upper Peninsula of Michigan.
Beetles may be less successful
in attacking healthy, vigorous trees in rural forests and this may reduce
the density
of beetles.
Ash trees widespread, but patchy
in location and therefore escapes from the beetle are possible.

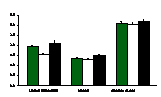
Green, white, and black ash are shown by
appropriately colored bars. SE is indicated by error bars. P-values are given for significant
differences between species for each value. *
indicates significant site*species interaction. St indicates that site was a significant
factor. Sp indicates that species was a
significant
factor.
St & Sp,
P = <0.0001
St, P =
<0.0001
St, P =
<0.0001
*, P = <0.0001
St, P =
<0.0001
*, P = 0.0056



*, P =
<0.0001
*, P =
0.0003
Tree-level
measurements include:
Height (m)
DBH (cm)
Uncompacted live crown ratio (ULCR; % of
tree)
Crown density (%)
Crown foliage transparency (%)
Crown dieback (%)
Light exposure (number of sides)
Vigor (category; 1 = healthy to 6 = dead)
Crown class (category; 1 = open grown to 5 =
suppressed)
Summary data values by species